ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY:
- Elbow arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that has many applications in diagnosing and treating elbow conditions in the throwing athlete
ADVANTAGES:
- Through small incisions around the elbow a camera is introduced into the elbow which allows complete inspection of the elbow. Arthroscopic techniques have many advantages including smaller incisions, minimal soft tissue trauma, less post-operative pain, faster healing time and earlier return to play than traditional open procedures
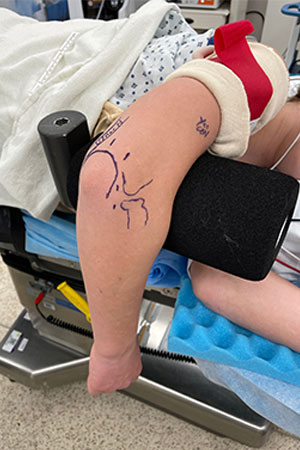
Standard Arthroscopy Portals Used to Access the Elbow Joint
TREATMENT:
- The mechanics of throwing make throwers susceptible to several unique elbow conditions which can be treated arthroscopically including:
- Posterior Medial Impingement/Valgus Extension Overload
- As the elbow is forced into extension at the end of throwing cycle, there is a shearing force across the back of the elbow at the olecranon. This repetitive loading can lead to formation of bone spurs (osteophytes) and pain along the posterior medial aspect of the elbow
- Throwers will typically describe pain at follow-through and may have a decreased ability to fully straighten the arm. They may also report mechanical symptoms such as catching, locking or popping in the elbow
- Bone spurs can be removed or debrided through elbow arthroscopy
- Osteochondritis Dissecans:
- Fragmentation or weakening of the cartilage along the capitellum in the elbow can occur secondary to repetitive force associated with activities such as throwing and gymnastics
- This can lead to swelling, loss of motion, “catching” of the elbow and pain along the outside of the elbow
- Elbow arthroscopy can be utilized to address the damaged cartilage
- Removal of Loose Bodies
- Small fragments of bone or cartilage can dislodge and float inside the joint. These can arise from injury or repetitive stress associated with throwing
- These loose fragments can cause pain, locking, catching or loss of motion in the elbow
- Elbow arthroscopy can remove free floating fragments from within the joint through small incisions
- Symptomatic Plica
- Plica is a benign thickening of the elbow capsule that can cause pain or clicking within the elbow in a select group of patients
- Symptomatic plicae are a rare cause of elbow pain in the throwing athlete
- Elbow arthroscopy allows for full assessment of the elbow and excision of symptomatic plica can be performed anthropically





- Posterior Medial Impingement/Valgus Extension Overload
POST OP:
- Dr. Nelson performs elbow arthroscopy as an outpatient procedure under regional anesthesia. Postoperatively the patient is placed into a sling until all short-term numbing medication has worn off. Self-directed therapy is typically initiated on the first postoperative day to help decrease swelling and regain motion. A formal therapy protocol is initiated 7-14 days after surgery based on the diagnosis and treatment. A return-to-throwing program varies by diagnosis, treatment and player’s position. This is typically between 6-12 weeks after range of motion and strength have fully recovered.
Dr. Nelson performing an elbow arthroscopy for capitellar OCD lesion
Arthroscopic Examination of Capitellar OCD Lesion
Dr. Nelson performing arthroscopic removal of loose body from the elbow
Arthroscopic Removal of Loose Body
Dr. Nelson performing arthroscopic excision of symptomatic plica
Dr. Nelson performing an elbow arthroscopy for evaluation of posteromedial impingement with excision of “bone chips”